“Teaching kids how to feed themselves and how to live in a community responsibly is the center of an education.” – Alice Waters
TweetTable of contents
Introduction
Fresh food is a cornerstone of healthy living, yet access to it remains limited in many parts of the world.
Addressing this challenge head-on, IFIZ Aquaponics offers education and resources aimed at empowering communities to grow their own sustainable fresh food.
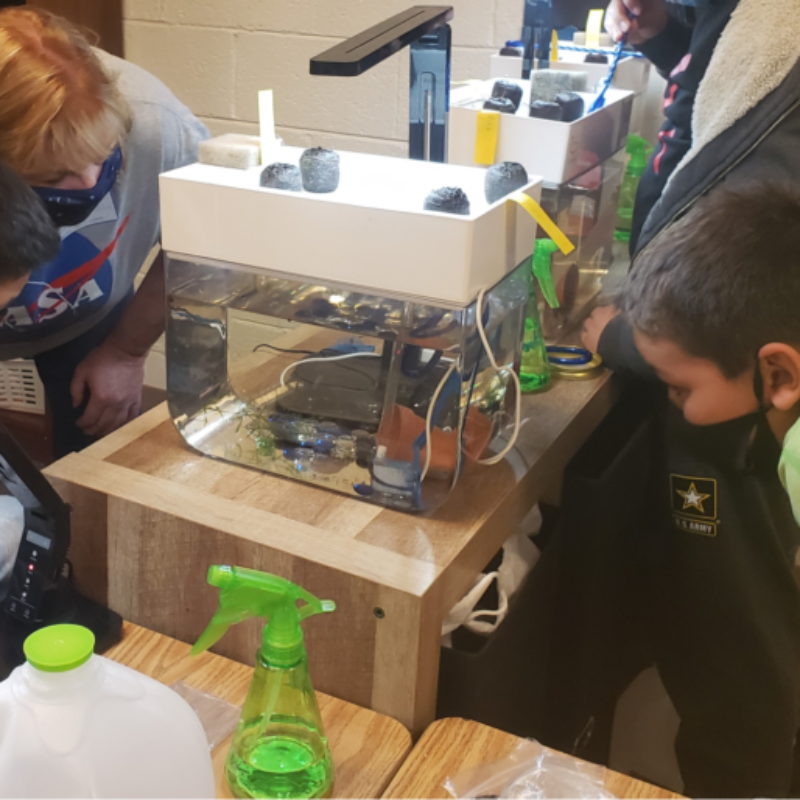
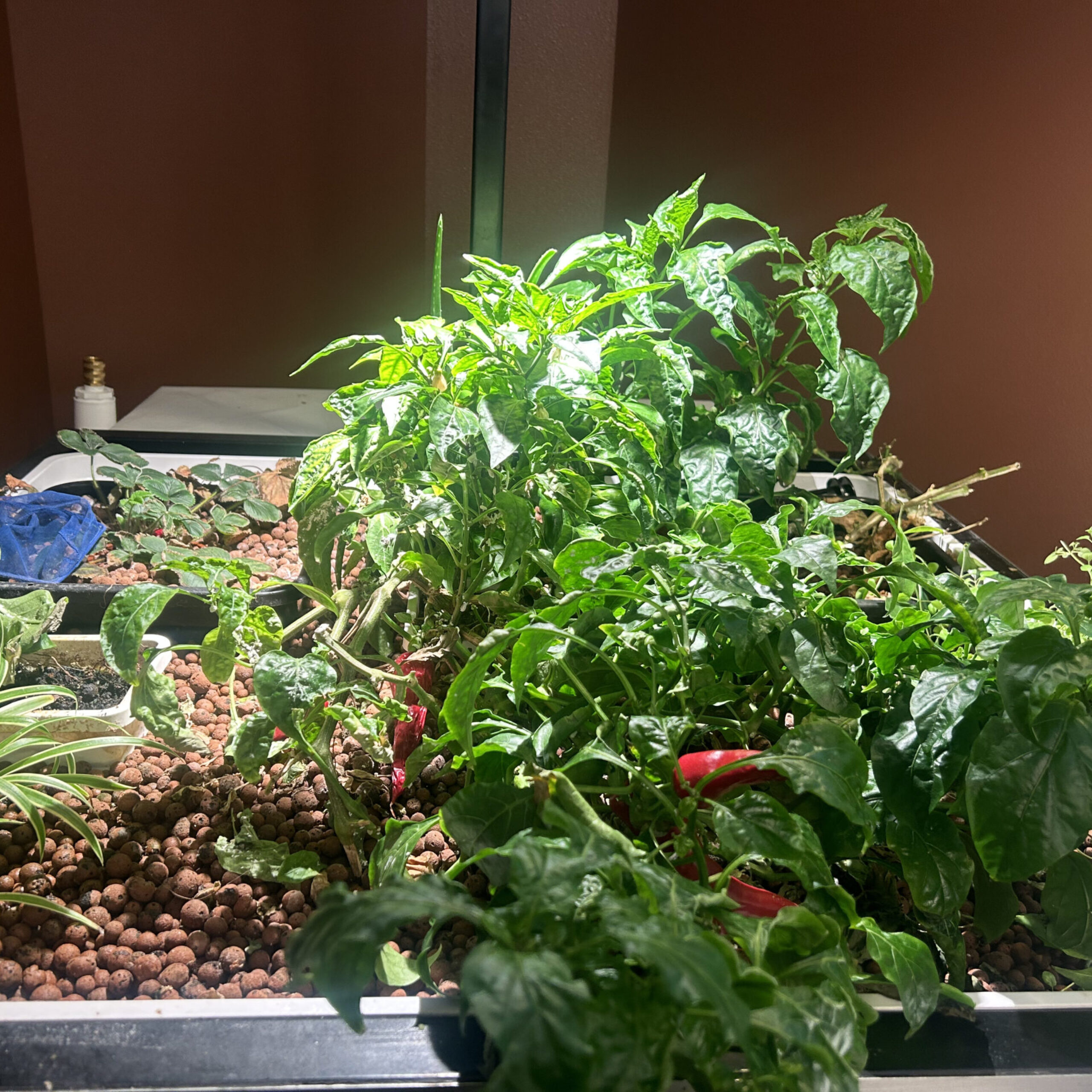
By combining aquaculture and hydroponics into aquaponic systems, IFIZ helps individuals and groups cultivate both fish and plants in a closed-loop ecosystem that maximizes efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.

What is Fresh Food Education?
Fresh food education equips people with the knowledge and skills to grow, harvest, and maintain nutrient-rich food sustainably.
Programs like those offered by IFIZ teach techniques that integrate technology, environmental stewardship, and food justice principles.
These initiatives are designed to create long-term solutions for food security while fostering community empowerment.
A Vision for Sustainability
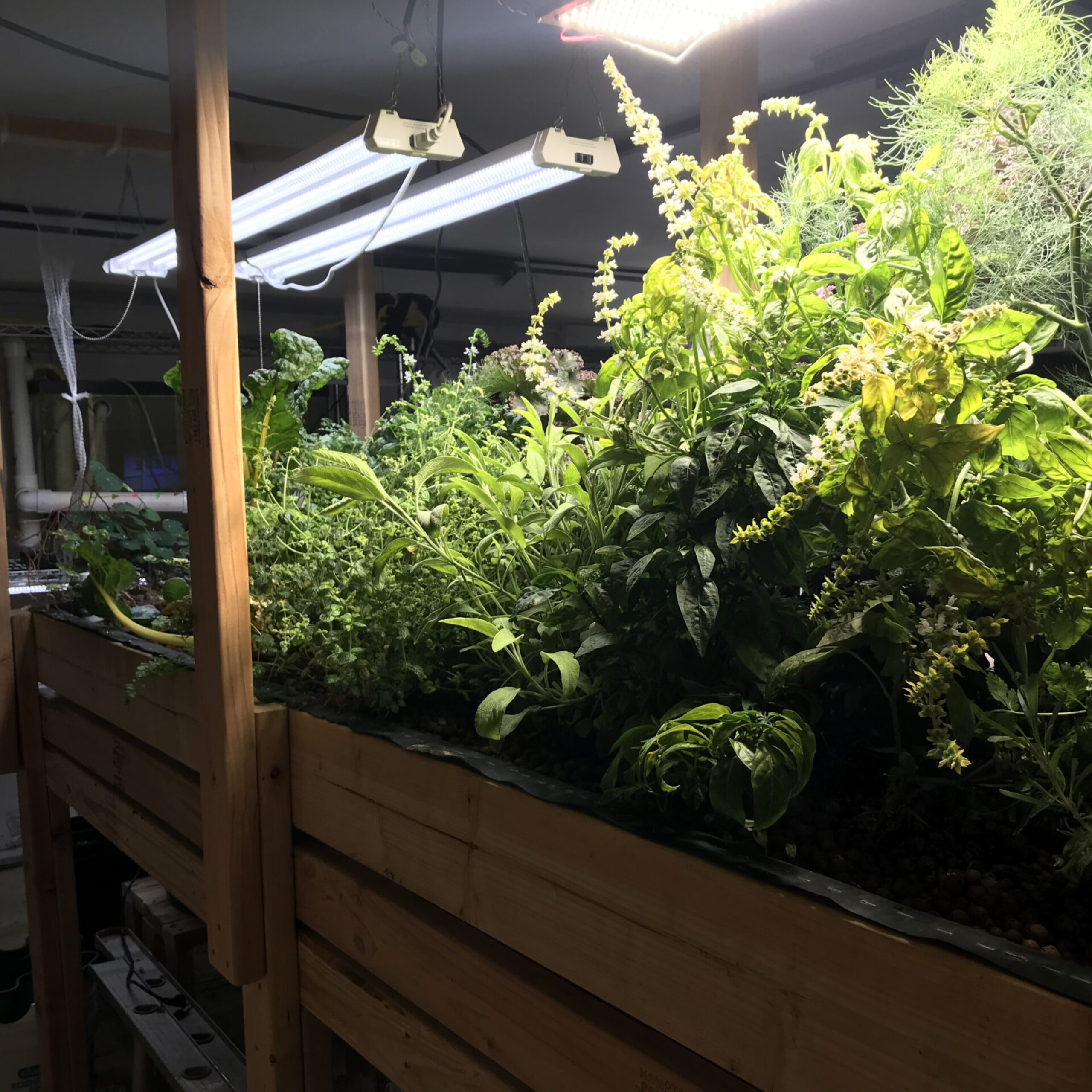
IFIZ focuses on making fresh food education accessible to all. Our aquaponic systems serve as both practical tools and educational platforms, demonstrating how small-scale ecosystems can provide healthy, locally-sourced produce and fish year-round.
This approach not only addresses food insecurity but also teaches participants about environmental conservation and resource efficiency.
Key components of IFIZ’s programs include:
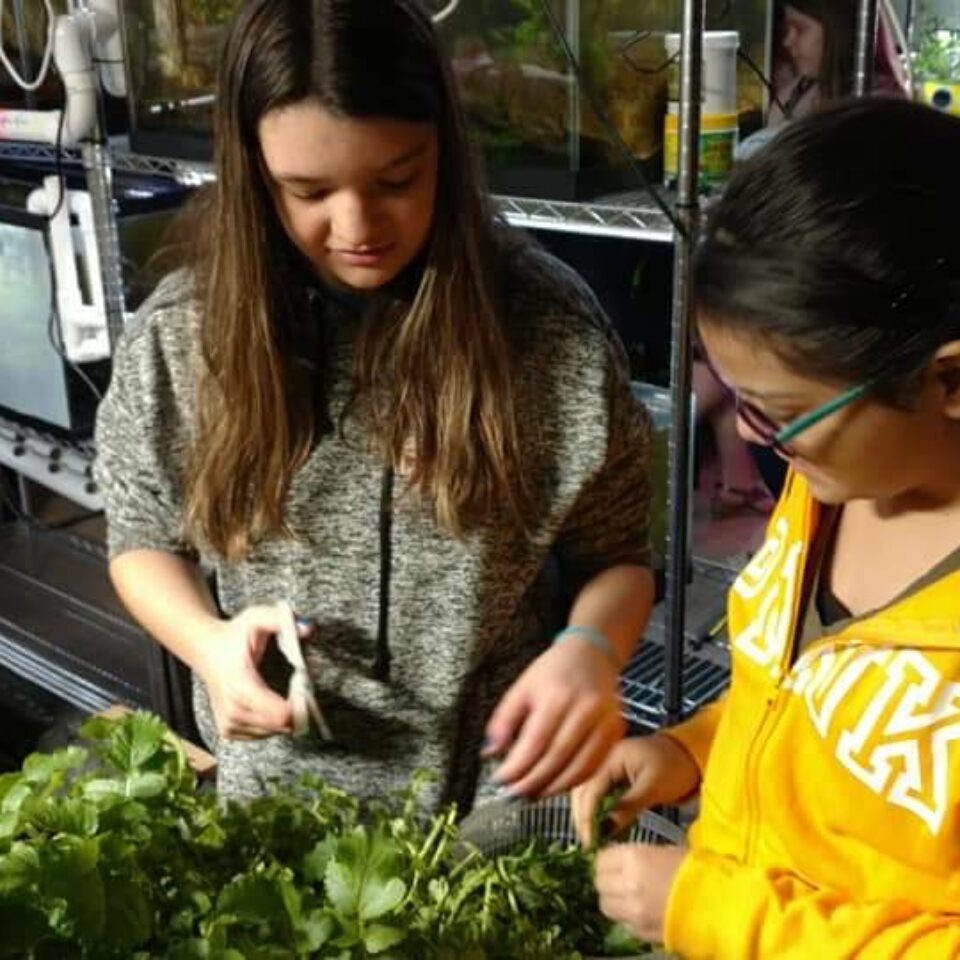
- Hands-On Learning: Participants build and maintain aquaponic systems, gaining real-world experience in sustainable agriculture.
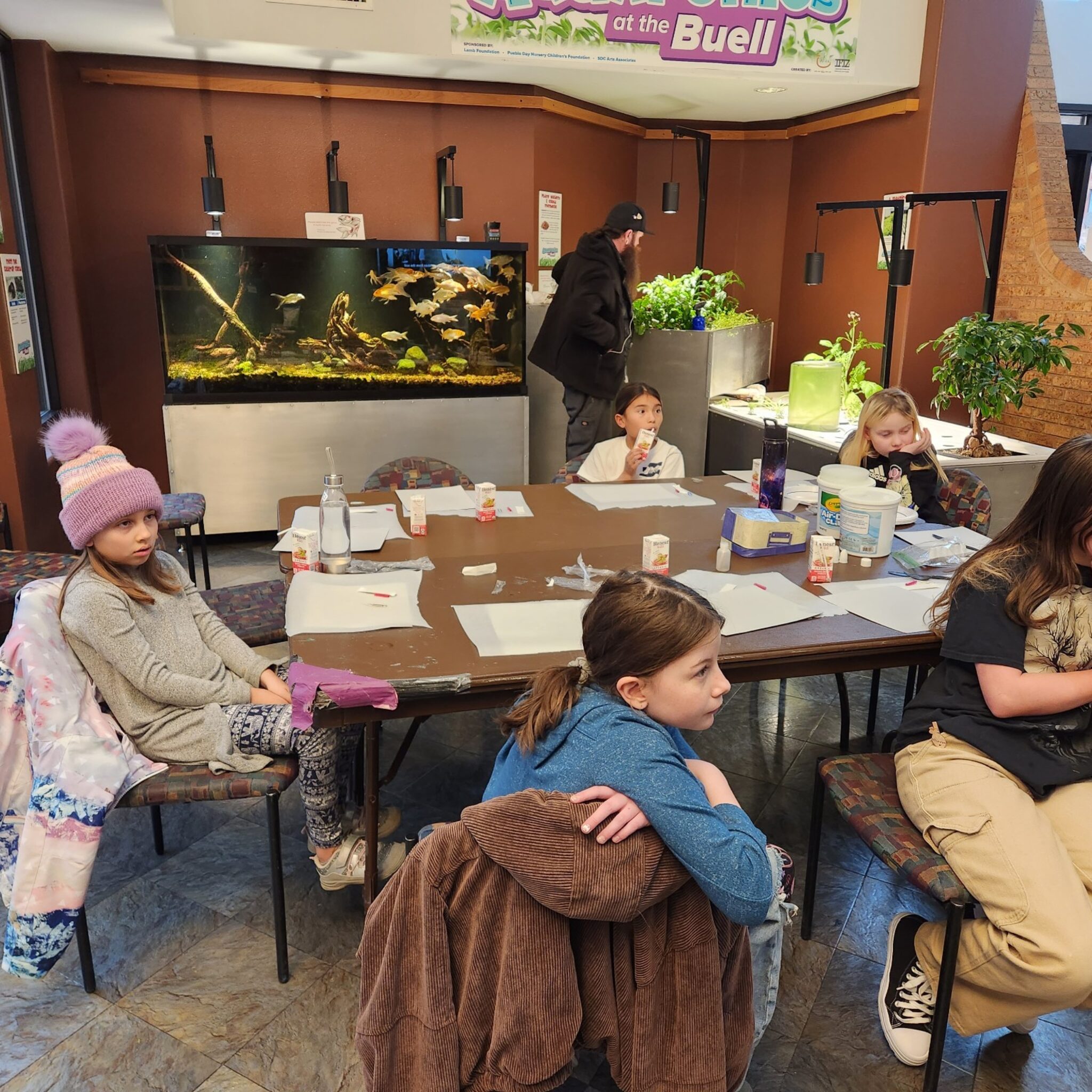
- Community Engagement: Programs are integrated into schools, food pantries, and urban areas, directly benefiting underserved populations.
- Environmental Impact: Aquaponics uses 90% less water than traditional farming and eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers or pesticides, supporting biodiversity and reducing pollution.

Real-World Impact of IFIZ Programs
IFIZ’s initiatives have brought fresh food education to various settings, including:
- Schools: Programs engage students in STEAM learning, teaching science, technology, and sustainability through aquaponics systems.
- Urban Areas: Vertical aquaponics systems have transformed urban spaces into productive farms, reducing food transportation costs and emissions.
- Food Pantries: Collaborations with organizations like RM SER enhance food access for marginalized communities by supplying fresh, nutritious food grown through aquaponics.
Steps to Start Fresh Food Production with Aquaponics
For those interested in starting their journey into aquaponics, here are simple steps:
- Understand the Basics: Learn how fish and plants work together in an aquaponic system.
- Choose a Location: Whether indoors or outdoors, ensure adequate light and space for the system.
- Set Up Your System: Install tanks, grow beds, and pumps while ensuring proper water flow and balance.
- Introduce Fish and Plants: Start with hardy fish like tilapia or goldfish and easy-to-grow plants such as lettuce or basil.
- Maintain the System: Regularly monitor water quality, feed the fish, and harvest plants as they mature.
Why Fresh Food Education Matters
Fresh food education fosters healthier lifestyles and more resilient communities.
By teaching sustainable practices like aquaponics, organizations such as IFIZ empower people to take control of their food sources. This not only enhances food security but also promotes environmental sustainability and economic development.
Conclusion
Fresh food education through aquaponics is an innovative solution to global food challenges.
Programs like those run by IFIZ help individuals and communities adopt sustainable practices while ensuring consistent access to nutritious food.
With aquaponics, the future of farming is brighter, greener, and more equitable.
For more on IFIZ Aquaponics and programs, visit the IFIZ page in the Programs tab of the menu.
FAQs
What is aquaponics, and how does it work?
Aquaponics is a sustainable farming method combining aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics (growing plants in water). Fish produce waste that is converted into nutrients for plants, while plants clean the water for the fish, creating a closed-loop ecosystem.
Why is fresh food education important?
It teaches sustainable practices that address food security, improve health, and protect the environment.
Can aquaponics be used in urban areas?
Yes, vertical aquaponics systems are ideal for urban spaces, transforming rooftops and vacant lots into productive green zones.
What are the environmental benefits of aquaponics?
Aquaponics conserves water, reduces chemical use, and supports biodiversity, making it an eco-friendly farming method.
What fish and plants are best for beginners?
Tilapia and goldfish are great starter fish, while lettuce, basil, and mint are easy-to-grow plants.
How can I learn more about aquaponics?
Join educational programs like those offered by IFIZ or explore online resources and community workshops.
Can fresh food be frozen?
Yes, fresh food can be frozen to preserve its quality, nutrients, and taste for a longer time. However, freezing certain foods may slightly alter their texture, so proper preparation, like blanching vegetables, can help maintain their freshness.
Why is fresh food important?
Fresh food is important as it provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants needed for a healthy body. It supports physical well-being, reduces the risk of chronic diseases, and contributes to a balanced diet, promoting long-term health and vitality.
Why is fresh food better than processed?
Fresh food is better than processed food because it is free from excessive salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats often found in processed items. Fresh foods are minimally altered, making them more nutritious and beneficial for health, while processed foods can contribute to weight gain, heart disease, and other health issues over time.
The I Will Projects, a 501c3 Non-Profit, promotes diverse solutions for global challenges. Our IFIZ education programs, emphasizing aquaponics, and insect farming, empower communities through knowledge, collaboration, and sustainable innovation.













