“One of the sustainable approaches to food security is sustainable agricultural practices.” ― Lailah Gifty Akita
Tweet
Table of contents
Introduction
In a world grappling with dwindling natural resources, escalating population growth, and the urgent need for sustainable food production, an innovative and eco-friendly system has emerged as a game-changer: aquaponics.
This groundbreaking agricultural technique combines aquaculture (the cultivation of fish) with hydroponics (the cultivation of plants in water) to create a harmonious and self-sustaining ecosystem.
By harnessing the power of nature’s interconnectedness, aquaponics has proven to be a revolutionary method of growing food that addresses multiple challenges simultaneously.
In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of aquaponics, exploring how it works, its advantages over traditional farming methods, and the significant impact it has on the way food is produced.
This is a cutting-edge food revolution that is transforming a sector of agriculture and offering a sustainable pathway to feed our growing global population.

Water Efficiency
As the global population grows and climate change affects water availability, efficient water usage has become increasingly important for farmers worldwide. Aquaponics, a sustainable farming system that combines aquaculture and hydroponics, is gaining popularity for its ability to grow crops and fish while minimizing water consumption.
Aquaponics employs a recirculating water system, which significantly reduces water usage. This system recycles water between fish tanks and hydroponic grow beds, eliminating the need for frequent water changes.
Unlike traditional farming methods that result in water loss through runoff or evaporation, aquaponics continuously recycles water, making it highly efficient.
By utilizing the same water repeatedly, aquaponics conserves water, reducing water usage by up to 90%. In contrast, traditional aquaculture systems require large amounts of freshwater for fish health, with the used water often discharged into the environment. Aquaponics mitigates this by recycling water throughout the system.
In aquaponics, plants are grown hydroponically, using a nutrient-rich recycled water medium. This eliminates the need for soil, enabling efficient water usage.
Unlike traditional gardening, where water can spill or evaporate from the soil, hydroponics provides plants with the necessary water for growth without wasting it.
Aquaponics also maintains water quality through proper management of water inflow and outflow.
Fish waste is converted into nutrients within the hydroponic system, promoting plant growth without the need for chemical fertilizers. This eliminates water contamination concerns associated with traditional farming methods.
Nutrient Recycling
Aquaponics efficiently recycles nutrients through the following process:
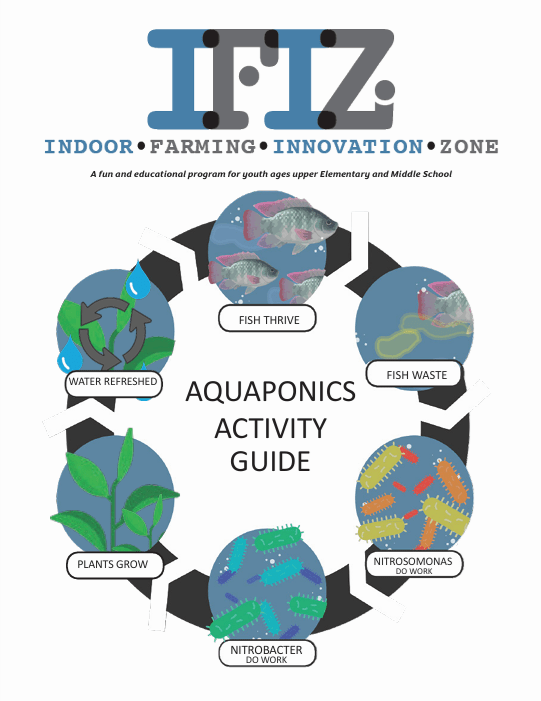
Fish waste acts as a nitrogen-rich fertilizer. Within the aquaponics system, fish are raised in a tank where they consume food and produce waste. This waste contains valuable nutrients, particularly nitrogen, which is essential for plant growth.
Beneficial bacteria play a crucial role in converting fish waste into plant food. The fish waste alone is not readily usable by plants.
The aquaponics system naturally contains helpful bacteria which transform the waste, initially converting ammonia (a toxic byproduct) into nitrite, and then into nitrate.
Nitrate is a form of nitrogen that plants can easily absorb and utilize.
Plants absorb the nutrients, simultaneously purifying the water.
In aquaponics, plants are cultivated hydroponically, without soil, in clay media beds or channels. These growing areas are flooded with the nutrient-rich water.
As plants absorb the nutrients, they effectively purify the water, eliminating excess nitrogen and other waste compounds.
After the plants have completed nutrient absorption and water purification, the clean water flows back into the fish tank. This closed-loop system ensures minimal waste and maintains the ongoing nutrient cycle.
The recycling of nutrients in aquaponics offers a multitude of benefits. It reduces waste, conserves water, and provides a sustainable source of fresh produce and fish.
Additionally, its closed-loop design makes it highly suitable for urban environments, where space and resources may be limited.
Increased Productivity
Aquaponics represents a groundbreaking and eco-friendly approach to cultivating plants and fish harmoniously within a self-contained system.
By merging the practices of aquaculture and hydroponics, aquaponics fosters a mutually beneficial relationship between plants and fish.
Besides its sustainable nature, this method offers numerous avenues for boosting productivity.
Firstly, aquaponics produces a higher yield of vegetables and plants compared to traditional farming of the same size.
The constant flow of nutrient-rich water ensures that plants receive the right nutrients at all times, promoting faster growth and quicker maturity.
Furthermore, aquaponic plants exhibit greater resistance to disease, pests, and environmental factors, resulting in lower crop loss.
Secondly, aquaponics requires less maintenance for plant care compared to soil-based farming.
The larger roots of aquaponic plants prevent tangling and suffocation, reducing the need for frequent maintenance.
Additionally, these plants require less watering, further decreasing overall crop maintenance time.
Moreover, aquaponics provides superior quality and freshness of produce.
The nutrient-rich environment allows plants to grow stronger and produce fruit more consistently, resulting in higher quality vegetables and fruits.
Since aquaponics can be practiced at home, individuals can enjoy freshly harvested produce, free from added chemicals, on a regular basis.
Furthermore, aquaponics is a water-efficient method, consuming only a fraction of the water used in traditional farming.
The continuous flow of water through the plants recycles it back to the fish tank, with minimal evaporation.
In contrast, soil-based farming requires frequent watering, making aquaponics a more sustainable and cost-effective option.
In conclusion, aquaponics offers numerous benefits, including sustainability and increased productivity.
By establishing a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants, aquaponics maximizes yields, reduces maintenance requirements, and saves water. This method represents one of the most sustainable ways to cultivate fresh and organic crops while increasing overall productivity.

Reduced Land Requirements
As the world’s population grows, the demand for food production continues to rise.
Traditional farming methods require large amounts of land, water, and fertilizers to produce crops.
However, aquaponics has revolutionized farming by creating a self-sustaining system. By utilizing fish waste to supply nutrients to plants and purify water for the fish, aquaponics creates a natural ecosystem that minimizes resource inputs.
One of the most significant advantages of aquaponics is its ability to reduce land requirements for food production.
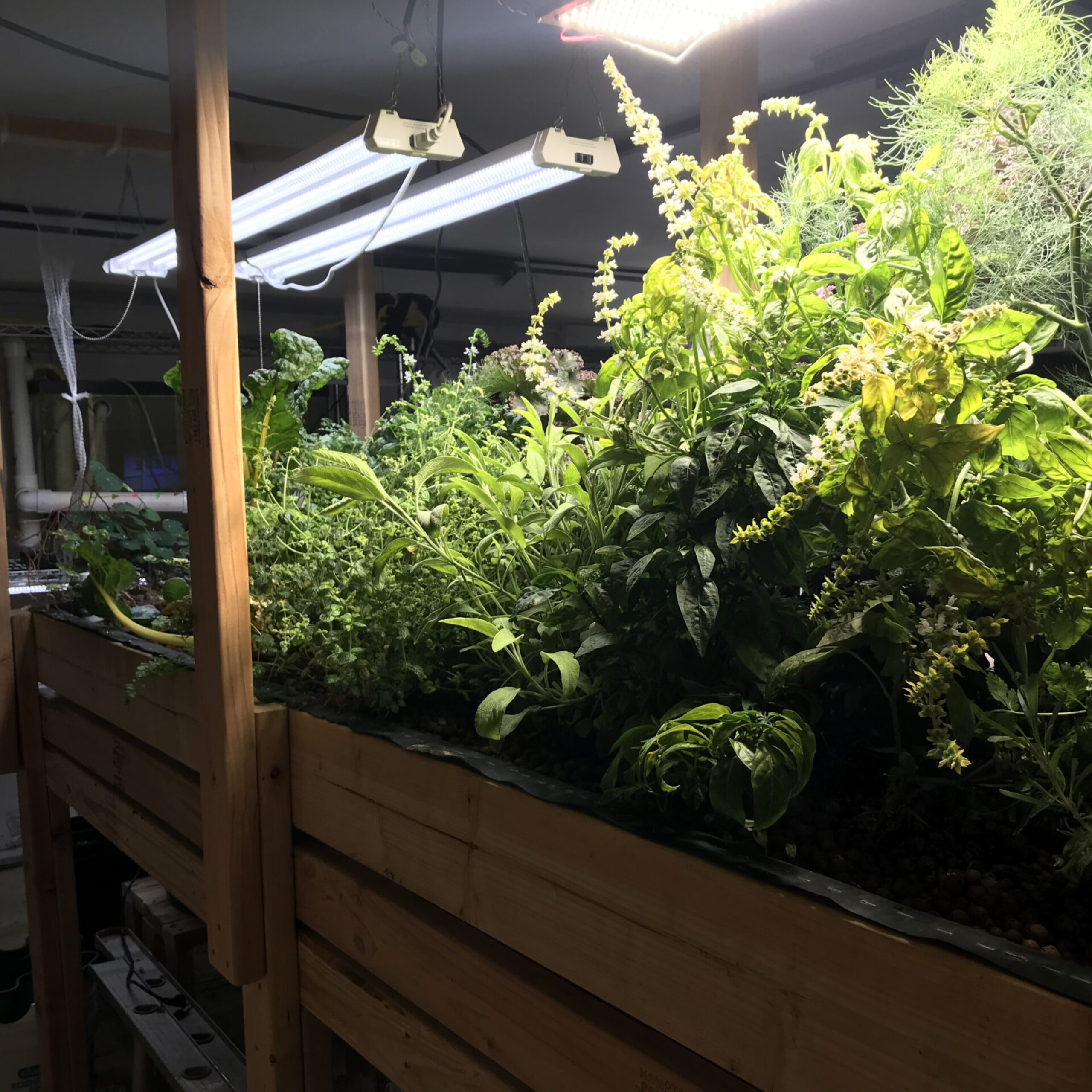
Unlike traditional farming methods, which requires ever expanding land use, aquaponics systems can be designed as vertical farming.
By growing crops in vertically stacked layers, less land is needed. This not only conserves space but also enhances efficiency, resulting in higher food production per square foot compared to traditional farming.
Aquaponics also allows for year-round crop production, regardless of the weather conditions.
The system can function indoors or outdoors under cover, enabling farmers to produce crops in regions with long winters or areas affected by harsh weather, which would typically hinder outdoor farming for extended periods.
Aquaponics represents an innovative and effective farming method that has transformed food production. It significantly reduces land requirements, mitigating environmental concerns such as soil degradation, deforestation, and resource depletion.
As the demand for food continues to increase, aquaponics offers a sustainable solution to address global food security while minimizing our environmental footprint.
Enhanced Sustainability
In the face of food security and climate change challenges, innovative farming methods are crucial.
Aquaponics, a combination of aquaculture and hydroponics, is gaining popularity as an environmentally sustainable and efficient approach to food production.
Conservation of Water
Aquaponics employs a closed-loop system that recirculates water, resulting in nearly 90% less water usage compared to traditional farming.
Water from the fish tank serves as a natural nutrient source for plants, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. The water then returns to the fish tank, where fish consume the waste from plant roots, maintaining water cleanliness.
Consequently, aquaponics significantly reduces water consumption compared to soil-based farming, which relies heavily on irrigation.
Preservation of Soil and Land
Traditional farming practices, including the use of heavy machinery and tilling, can cause soil erosion and degradation. These issues lead to soil compaction, nutrient loss, and decreased productivity.
Aquaponics mitigates these concerns since soil is not used in the system. Instead, hydroponic techniques, such as growing plants on floating rafts or in trays with media like clay pebbles, are used.. This approach ensures that plant roots remain supported and undisturbed.
Limitation of Chemical Usage
Conventional farming frequently relies on manufactured chemical pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers to protect crops and maximize yields. However, these substances pose environmental risks and can negatively impact human and ecologic health.
In aquaponics, the system operates without the need for chemicals. The waste produced by the fish serves as a natural fertilizer, with essential nutrients added as necessary.
Moreover, the closed-loop nature of aquaponics minimizes the risk of contaminating nearby water sources.
Energy Efficiency
Aquaponics is an energy-efficient farming method. Traditional practices such as plowing, planting, and harvesting demand substantial energy and labor.
In aquaponics, the system is automated, resulting in minimal energy consumption.
Additionally, the use of LED grow lights enables precise control over plant growth while minimizing energy usage.
Aquaponics represents an innovative and environmentally sustainable approach to farming.
By reducing water consumption, preventing soil erosion and degradation, minimizing chemical usage, and promoting energy efficiency, aquaponics offers solutions to many challenges associated with traditional farming.
As we confront food security and climate change concerns, aquaponics presents an exciting and promising path forward.
Community Engagement and Education
Aquaponics offers community engagement and educational benefits. It allows people to come together, work in teams, and foster a sense of community while constructing and maintaining the system.
The decision-making process of selecting crops promotes social interaction, healthy food awareness, and culinary exploration.
Moreover, aquaponics facilities can organize events and workshops to educate the public about sustainable farming practices, locally-sourced food, and employment opportunities.
In terms of education, aquaponics provides hands-on learning opportunities in science, technology, engineering, math, and sustainability.
Students gain knowledge about the nitrogen cycle, water conservation, and sustainable agriculture. They also develop life skills like responsibility, problem-solving, critical thinking, and teamwork by designing and managing aquaponics systems.
Additionally, aquaponics can be integrated into various subjects such as biology, environmental science, math, social sciences and business, allowing students to explore topics like the economics of aquaponics and its potential as a sustainable business model.
In conclusion, aquaponics extends beyond food production by facilitating community engagement and offering educational benefits. It promotes sustainable agriculture, life skill development, relationship-building, and provides opportunities for students to learn about science, technology, and the environment.
Aquaponics is a versatile and innovative system with wide-ranging impacts.
Climate Resilience
Climate change poses a significant environmental challenge today, impacting various aspects of our planet, including food production. Recognizing these effects, it is crucial to develop sustainable methods for producing food that can adapt and withstand these changes.
Aquaponics, an increasingly popular solution worldwide, offers climate resilience in food production.
This closed-loop system establishes a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants, fostering an ecosystem resilient to natural fluctuations.
Water conservation is a notable advantage of aquaponics.
The system is remarkably water-efficient, making it particularly suitable for drought-prone regions.
Compared to traditional farming methods, aquaponics requires only a fraction of the water since it continuously recycles and reuses water, minimizing waste and conserving resources.
Aquaponics also reduces the reliance on pesticides and herbicides.
With plants cultivated indoors or in controlled environments, the risk of pests and diseases is significantly lower.
Consequently, chemical treatments become less necessary, enhancing environmental friendliness and safety for consumption.
Another significant benefit of aquaponics lies in its flexibility and scalability.
These systems can be implemented in diverse settings, from small urban environments to large commercial farms.
Such versatility makes aquaponics a valuable tool in building climate resilience within communities grappling with food insecurity and environmental challenges.
Aquaponics offers multiple advantages for food production and climate resilience.
The growing method has proven its exceptional efficacy in cultivating sustainable and eco-friendly food.
By conserving water, reducing the need for chemicals, and establishing a flexible and scalable closed-loop system, aquaponics becomes an indispensable tool in addressing the climate change challenge.
Embracing aquaponics as the future of sustainable food production is a wise practice and offers many opportunities..
Conclusion
Aquaponics is truly revolutionizing the way we grow food, offering a sustainable and efficient solution to our ever-growing food demands.
This revolution is not just about growing food. It is a transformative force that promotes sustainability, self-sufficiency, and a healthier future for both the planet and its human inhabitants.
By embracing this food production approach, we can reduce the burden on the environment and create a harmonious partnership between nature and technology.
The future of farming is here, and it’s swimming alongside our plants in an aquaponic system.
The I Will Projects, a 501(c)3 organization serving communities since 2014, believes in multiple solutions to address global challenges. Our IFIZ education programs focus on general aquaponics, growing microgreens and sprouts, and insect farming. These programs empower communities by expanding knowledge, developing collaboration, and advocating for sustainable innovation. Our aim is to contribute to a regenerative food system, ensuring access to healthy food and recognizing food as medicine.